AI Agents
- AI Agents are intelligent assistants that understand context, reason through tasks, and adapt over time - helping automate complex business processes.
- AI that sees, hears and speaks: They process voice, images, video, and text enabling natural, human-like interactions and automating tasks once limited to human perception.
- Built for the real world: From finance to healthcare, we’ve implemented AI Agent ecosystems across all industries that solve integration, compliance, and performance challenges with ease.
- Secure by design: Our AI Agents are built with encrypted memory, role-based access, and auditable controls to protect your data without slowing you down.
- Any infrastructure, any workflow: Whether you're on-prem, hybrid, or in the cloud, our agents seamlessly connect to existing systems and workflows.
- Microsoft and Cazton: We work closely with OpenAI, Azure OpenAI and many other Microsoft teams. Thanks to Microsoft for providing us with very early access to critical technologies. We are fortunate to have been working on GPT-3 since 2020, a couple years before ChatGPT was launched.
- Trusted by industry leaders: We partner with Fortune 500s, global enterprises, and high-growth startups across sectors. Our clients include Microsoft, Google, Broadcom, Dell, Bank of America, Thomson Reuters, and more - organizations that demand both innovation and accountability.
The Executive Automation Challenge
Your current automation initiatives have delivered impressive results: streamlined processes, reduced manual work, and improved efficiency. Yet you face a growing challenge: complex business workflows that require human judgment, cross-system coordination, and adaptive decision-making. Traditional automation tools cannot handle these sophisticated scenarios, creating operational bottlenecks that limit your organization's growth potential.
Are you finding that your most valuable processes still require extensive human oversight? Do exceptions and edge cases consistently break your automated workflows? These challenges signal the need for a more intelligent approach; one that combines the efficiency of automation with the adaptability of human reasoning.
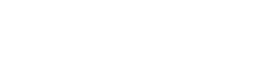
AI Agents represent the next step forward. These autonomous systems can perceive, decide, and act, learning from context, navigating ambiguity, and evolving with each interaction. We help organizations design, implement, and scale AI Agent ecosystems tailored to real-world business needs, ensuring a secure, compliant, and measurable transformation from pilot to production.
Understanding AI Agents
Imagine an autonomous agent as a digital entity with a brain, memory, speech and listening capabilities, and a comprehensive set of tools at its disposal. The brain, powered by Large Language Models (LLMs), orchestrates the agent's actions, while the memory stores and retrieves information, and the tools extend the agent's capabilities beyond its inherent functions.
Smarter interactions with images, voice, and video: Today's AI Agents combine Large Language Models with Large Vision Models (LVMs), creating systems that can see, hear, and converse like humans. This multimodal capability transforms how organizations approach complex workflows that previously required human sensory perception and judgment.
These agents can:
- See: Analyze visual data, recognize patterns in documents, images, and video streams, providing insights that drive decision-making.
- Hear: Process spoken language, understand voice commands, and participate in natural conversations.
- Talk: Engage in human-like interactions, provide explanations, and communicate findings across teams.
The key differentiator lies in their ability to understand context, make decisions, and learn from outcomes. While traditional automation follows predetermined rules, AI Agents can interpret ambiguous situations, access multiple data sources, and adjust their approach based on real-time conditions, all while maintaining human-like communication capabilities.
Since 2012, we have been at the forefront of this AI revolution, building AI-powered autonomous agents. Since 2020, we have been pioneering the use of generative AI, developing agents that not only perform tasks but also learn and adapt to new challenges, ensuring that your business stays ahead of the competition.
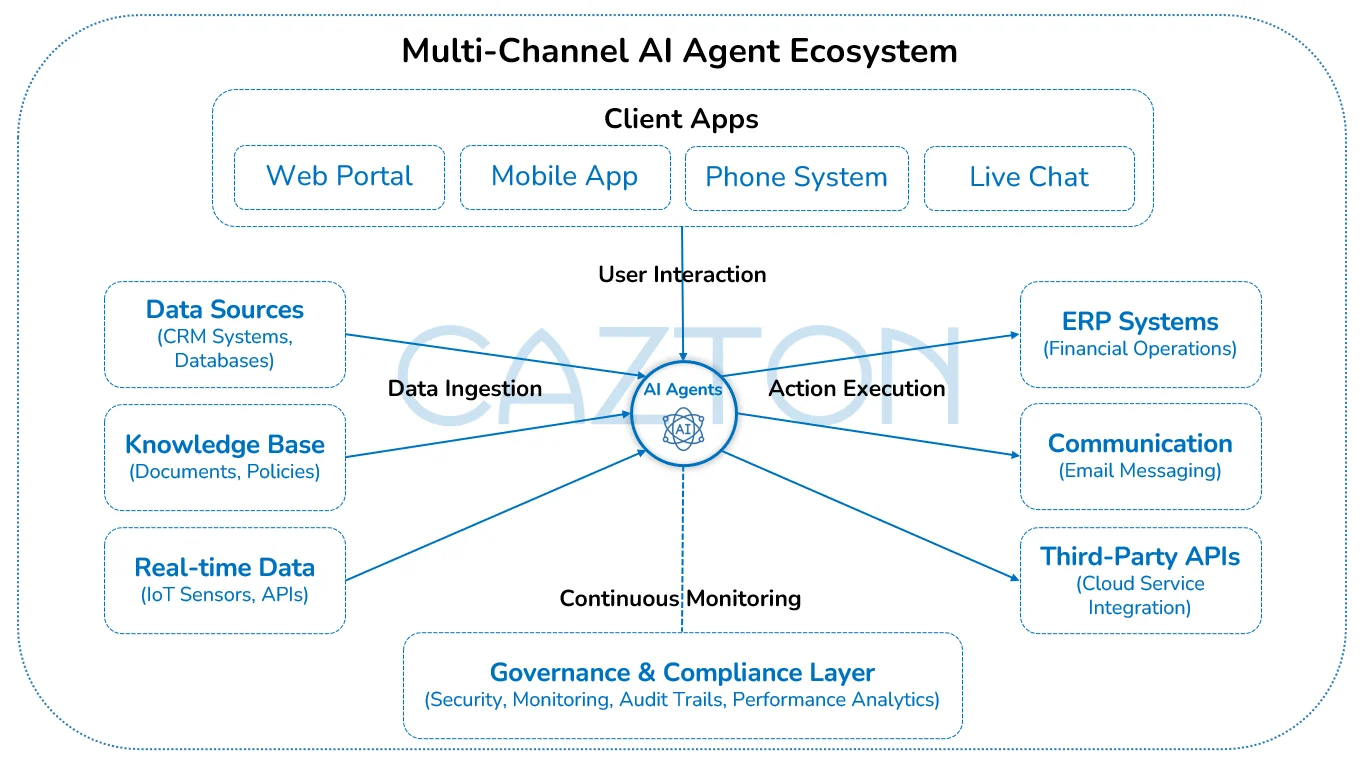
How AI Agents Think and Act
Understanding AI Agent architecture helps executives appreciate their transformative potential. These systems operate through interconnected components that mirror human cognitive processes while providing enterprise-grade reliability and scalability.
- Planning and execution: AI Agents determine the sequence of actions needed to achieve business goals through sophisticated planning mechanisms. They can organize tasks hierarchically, with high-level objectives broken down into specific, executable sub-tasks. This structured approach allows agents to navigate complex workflows efficiently while maintaining focus on strategic outcomes.
- Adaptive learning strategies: Rather than following rigid programming, AI Agents employ dynamic learning approaches that adjust based on real-time feedback and environmental changes. They learn from interactions, continuously refine their decision-making processes, and improve performance without requiring manual reprogramming.
- Memory systems: Enterprise AI Agents utilize both short-term contextual memory for immediate task execution and long-term memory systems that store knowledge across extended periods. This dual-memory approach enables them to maintain context during complex interactions while accessing historical data and learned experiences from previous engagements.
- Reflection and refinement: Like skilled professionals reviewing their work, AI Agents analyze past actions, identify improvement opportunities, and refine their strategies. This continuous learning loop ensures agents not only execute tasks but also enhance their performance over time.
Does your organization struggle with processes that require both immediate decision-making and long-term learning? AI Agents address this challenge by combining immediate responsiveness with continuous improvement capabilities.
What Most People Get Wrong About AI Agents
Large organizations across various industries often encounter several major misconceptions about AI agents that can hinder their adoption and effective use. Some of these misconceptions are listed below:
- AI Agents will replace human jobs: Many organizations fear that AI agents will fully replace human roles. In reality, AI agents are designed to augment human capabilities by automating routine, repetitive tasks, freeing employees to focus on higher-value, strategic, creative, or empathetic work. AI agents act as collaborators, not replacements.
- AI Agents are fully autonomous and require no oversight: There is a belief that AI agents can operate entirely independently, handling any task without human intervention. The truth is that AI agents, especially in complex or regulated environments, require training, oversight, and guardrails to perform effectively. They are best suited for narrow, well-defined tasks and often need human approval or monitoring for critical decisions.
- AI Agents compromise data privacy and security: Some organizations hesitate to adopt AI agents due to concerns about data privacy and security. However, well-designed AI systems can be implemented with robust privacy controls, on-device processing, and strict access boundaries, preserving data security while still delivering value.
- AI Agents are prohibitively expensive for mid-sized or large organizations: The perception that AI agents are only affordable for large enterprises persists. In reality, AI solutions have become scalable and cost-effective, with pricing models that cater to organizations of various sizes. Many businesses achieve a strong return on investment by automating high-impact processes.
- AI Agents are unpredictable and uncontrollable: Some believe that AI agents are inherently unpredictable and may act in ways that are difficult to control. In practice, AI agents operate within predefined rules and guardrails, and their autonomy can be adjusted based on the complexity and risk of the task.
- AI Agents can handle any complex or unusual request: Organizations sometimes overestimate the capabilities of AI agents, expecting them to manage highly complex or ambiguous situations. AI agents excel at repetitive, rule-based tasks but struggle with nuanced judgment, emotional context, or novel scenarios that require human expertise.
- AI implementation must start big: There is a misconception that organizations must launch large-scale, public-facing deployments to benefit from AI agents. In reality, starting small, by automating internal processes, allows organizations to build experience and scale gradually, leading to more effective and sustainable adoption.
At our core, we help organizations cut through the noise and approach AI Agents with clarity and purpose. From identifying the right use cases to ensuring secure, scalable implementation, we guide you every step of the way, turning common concerns into competitive advantages.
Case Studies
Customer Service Transformation
- Challenge: A large financial institution manages millions of customer interactions annually across a wide range of products and services. Customer service teams had to manually navigate multiple legacy systems to retrieve account details, transaction histories, and support documentation. This led to delays, inconsistent responses, and high agent fatigue, especially during peak service periods.
- Solution: We designed and deployed AI Agents within the customer service platform to automate contextual data retrieval and real-time response generation. Our solution enabled seamless integration with legacy systems using standardized APIs, allowing agents to instantly access account data, transaction histories, and support options. The AI Agents interpreted customer queries in natural language, handled routine inquiries autonomously, and routed complex issues to human teams with complete contextual awareness.
- Business impact: The organization experienced faster resolution times and improved consistency across customer interactions. Agents were able to focus on higher-value conversations, while the AI Agent handled repetitive information gathering and basic inquiries. The platform scaled efficiently, increasing customer demand, and maintaining service quality.
- Tech stack: React-based dashboards, Node.js APIs, PostgreSQL, Redis, Elasticsearch, Ionic-based mobile applications for field support.
Financial Transaction Processing
- Challenge: This multinational payment processing company processed millions of financial transactions each day, requiring complex validation against compliance standards and fraud detection rules. Multiple disconnected systems created data silos, resulting in slow updates, duplicated effort, and significant maintenance overhead. Operational risk increased as teams struggled to keep pace with shifting regulatory demands.
- Solution: We architected and implemented a scalable AI Agent framework to unify transaction validation, fraud detection, and compliance workflows. By securely exposing transaction metadata and verification logic as reusable components, we enabled the agents to analyze patterns in real time and dynamically adjust processing rules. Our approach simplified compliance updates and reduced operational risk through flexible, secure integrations.
- Business impact: Transaction processing became more consistent and adaptable, reducing errors and operational risks. The organization could quickly update processing logic to meet evolving regulatory and business requirements, improving agility and reducing manual intervention.
- Tech stack: Angular dashboards, .NET APIs, SQL Server, MongoDB, Microsoft Fabric, and secure integration with external financial services.
Healthcare Operations
- Challenge: A regional hospital network was overwhelmed by the volume of patient appointments, records, and claims distributed across several locations. Staff spent excessive time on manual data entry and verification, which often led to delays, administrative errors, and a negative impact on patient satisfaction. Critical insights were locked within siloed systems, slowing decision-making.
- Solution: We introduced AI Agents to streamline operational workflows across appointment scheduling, patient record access, and insurance processing. By integrating with electronic health record systems, we enabled real-time data validation, automated reminders, and clinical summarization tools for healthcare providers. Our implementation significantly reduced manual tasks while supporting regulatory compliance and improving patient care quality.
- Business impact: Operational efficiency improved as repetitive administrative tasks were automated. Staff could focus more on patient care, and data accuracy increased, reducing delays and improving patient satisfaction. The system adapted to changing regulations and workflows, supporting continuous improvement.
- Tech stack: Reactjs, Voice AI Pro, Java-based APIs, Python-based AI orchestration, PostgreSQL, Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB (vCore), and integration with electronic health record systems.
Manufacturing Process Optimization
- Challenge: A global automotive parts manufacturer relied on manual oversight to monitor complex production lines. Static scheduling and delayed issue detection led to unplanned downtime, quality lapses, and reduced throughput. The absence of real-time insights made it difficult to respond to disruptions quickly or optimize workflows for efficiency and sustainability goals.
- Solution: We implemented AI Agents that monitor and optimize production lines in real time, enabling predictive maintenance, quality control, and energy efficiency. Leveraging sensor and vision data, our solution identified performance issues before failures occurred, dynamically adjusted production schedules, and automated defect detection, resulting in smarter, more adaptive operations across global facilities.
- Business impact: The manufacturer reduced unplanned downtime and improved product quality. Production scheduling became more agile, and inventory and supply chain decisions were optimized. Energy usage was managed more efficiently, supporting sustainability goals.
- Tech stack: Blazor, Python-based AI for predictive analytics, .NET-based APIs, SQL Server, Kafka, OpenAI, Databricks, Apache Spark, Kubernetes, Terraform, and integration with IoT sensors and vision systems.
Retail Experience Enhancement
- Challenge: A national retail enterprise lacked real-time visibility into customer behavior and inventory across locations. Marketing and operations teams could not personalize the shopping experience or optimize stock placement effectively. This resulted in missed revenue opportunities, high return rates, and elevated inventory costs.
- Solution: We deployed AI Agents to drive real-time personalization, inventory intelligence, and customer experience innovation. Our solution connected customer behavior data, historical purchases, and inventory systems to generate personalized recommendations, power virtual try-ons, and optimize stock levels. We also embedded proactive analytics to help business teams anticipate demand and reduce return rates.
- Business impact: The retailer achieved higher customer engagement and increased sales through personalized experiences. Inventory management became more efficient, reducing waste and operational costs. Virtual try-on capabilities lowered return rates and improved the overall shopping journey.
- Tech stack: Vue-based e-commerce platforms, Node.js APIs, PostgreSQL, Redis, Azure OpenAI, Apache SOLR, Microsoft Fabric, PyTorch, and integration with augmented reality (AR) tools.
Multi-Agent System: When AI Agents Collaborate
In advanced enterprise environments, AI doesn’t work alone. Multi-agent systems bring together multiple specialized AI Agents that coordinate, communicate, and solve problems collaboratively. This model enables distributed intelligence where digital agents operate independently but work as a team to handle complex workflows.
- Specialized agents for complex tasks: Each agent in a multi-agent system focuses on a specific function for e.g. finance, compliance, customer interaction, or scheduling. By assigning responsibilities, the system mirrors how real teams divide work and operate more efficiently.
- Seamless agent-to-agent collaboration: Agents don’t work in silos. They share information, coordinate actions, and negotiate outcomes to solve problems too complex for a single agent, just like specialized departments in an organization.
- Real-time adaptation across the system: Multi-Agent Systems continuously adapt to changing business needs. If one agent detects a shift, like a new compliance rule or customer behavior, it signals others to adjust in sync, keeping workflows responsive and up to date.
- Human-AI Synergy: The best systems combine machine speed with human judgment. Agents handle data processing, pattern recognition, and task execution ,while humans make strategic calls, drive innovation, and manage relationships.
- Scalable, modular intelligence: With a multi-agent system, you don’t need to build one giant agent ,you grow an intelligent workforce over time. New agents can be added for new use cases, making the system scalable and future-proof without rewiring everything.
How does your organization currently handle complex workflows that require multiple types of expertise? AI Agent ecosystems can transform these processes by enabling specialized digital workers to collaborate seamlessly while maintaining human oversight. Ready to transform your workflows with intelligent, collaborative AI? Let’s build your multi-agent strategy together.
Implementation Strategy: From Vision to Value
Successful AI Agent implementation requires a strategic approach that balances innovation with operational stability. Organizations cannot simply deploy AI Agents and expect immediate results; the technology must be carefully integrated with existing systems, processes, and organizational culture.
- Phase-based implementation minimizes risk while building organizational capability. We begin with focused use cases that demonstrate clear value, then expand capabilities based on proven success and lessons learned. This approach allows your teams to develop confidence with AI Agent technology while delivering measurable business outcomes.
- The implementation process addresses both technical and human factors. While AI Agents can see, hear, and speak, their effectiveness depends on thoughtful integration with human workflows. We design implementations that enhance human capabilities while maintaining the personal touch that customers and employees value.
- Integration complexity represents the primary challenge in enterprise AI Agent deployment. Your existing systems, data architectures, and business processes create unique requirements that cannot be addressed through generic solutions. We design custom integration strategies that leverage your existing technology investments while enabling AI Agent capabilities.
- Governance frameworks ensure AI Agent operations align with your organizational policies, compliance requirements, and risk management standards. These frameworks establish monitoring protocols, performance metrics, and control mechanisms that maintain operational oversight while enabling autonomous functionality.
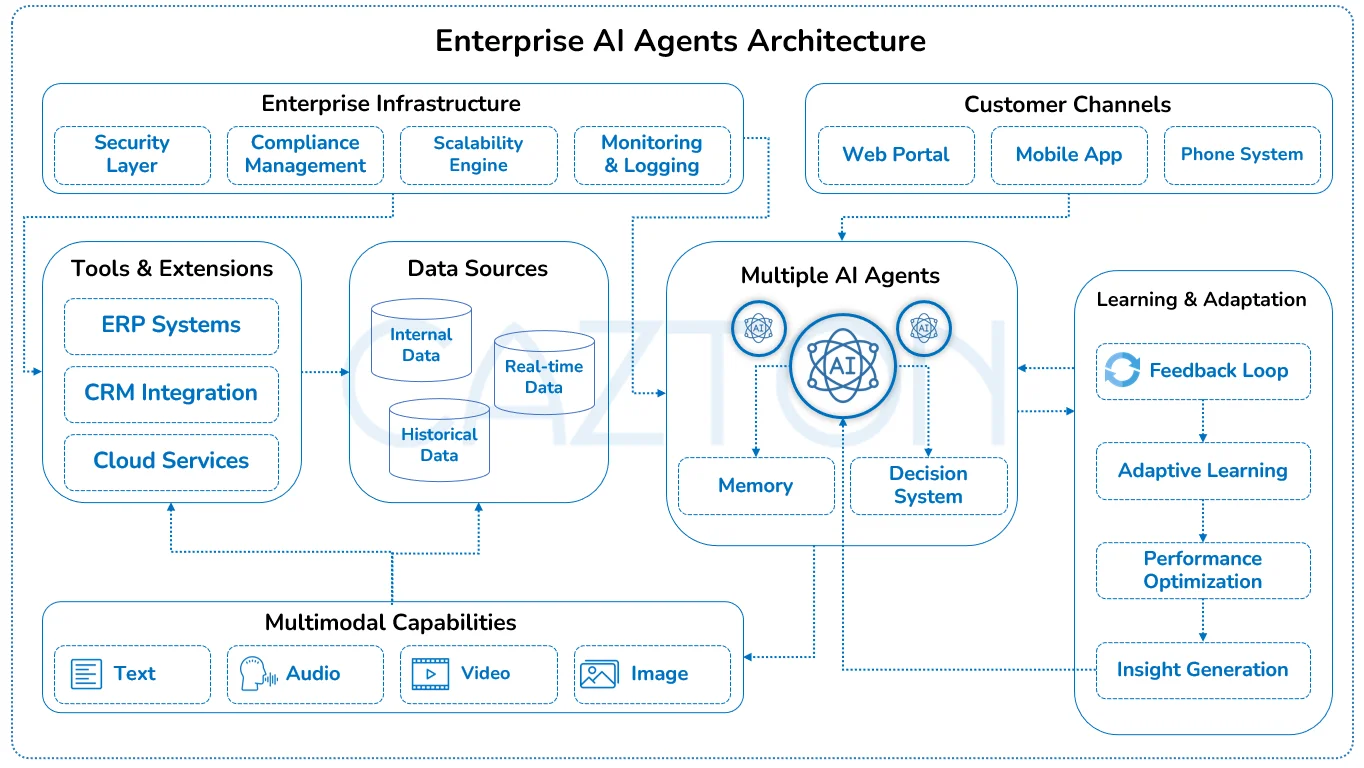
Enabling Advanced AI Agent Capabilities at Scale
Deploying AI Agents at the enterprise level goes far beyond basic automation. It requires a foundation that not only supports advanced capabilities but also delivers the infrastructure to scale them securely and efficiently.
- AI that sees, hears, and speaks: AI Agents can process text, voice, images, and video, enabling tasks like document review, visual inspection, and natural conversations.
- Contextual learning: Agents continuously improve by learning from interactions, reducing the need for manual updates and increasing long-term value.
- Understanding across formats: By combining visuals, spoken language, and context, AI Agents handle complex situations that traditional automation cannot.
- Scalable architecture: Systems are built to grow with your needs: supporting more users, more data, and more use cases without compromising performance.
- Backend integration: Secure APIs and real-time data pipelines connect AI Agents to your existing tools and systems for reliable, consistent results.
- Low-latency processing: Infrastructure is optimized for speed delivering fast, responsive decision-making even in high-demand environments.
- Security and compliance: Strong safeguards ensure AI Agents meet regulatory standards and protect sensitive business and customer data.
- Future-ready design: The foundation supports evolving technologies, changing business needs, and long-term innovation without costly rework.
We help organizations design intelligent systems that can see, hear, understand, and learn,just like humans. From seamless integration to secure, scalable infrastructure, we turn advanced AI capabilities into real business outcomes. Whether you are enhancing customer service, automating workflows, or driving operational intelligence, our solutions are built for speed, trust, and future growth.
Future-Proofing AI Agent Investments
AI Agents deliver more than automation; they reshape how organizations operate, compete, and grow. Measuring their success involves tracking real business impact while ensuring your investment remains adaptable to future innovation.
- ROI through efficiency: AI Agents consistently reduce routine tasks sometimes by 40-60% and can cut error rates by 30-50%, driving faster processes, fewer mistakes, and lower costs across document processing, customer service, and workflow execution.
- Strategic value creation: By taking over repetitive work, AI Agents allow your teams to focus on strategic thinking, problem-solving, and customer relationships enhancing innovation and workforce satisfaction.
- Improved accessibility: Voice and vision capabilities expand usability for all users, including those with different needs or preferences, improving employee productivity and customer inclusivity.
- Real-time performance monitoring: We implement detailed analytics to track AI Agent performance, business impact, learning progression, and user satisfaction, enabling continuous improvement and stakeholder alignment.
- Scalable by design: Our implementations are built to grow. As your business expands, your AI Agent infrastructure easily adapts, adding new use cases, data sources, and integrations without disruption.
- Ready for tomorrow’s tech: From advanced multimodal reasoning to integration with IoT, AR, or robotics, your AI Agents are designed to evolve with emerging technologies, keeping you ahead of the innovation curve.
- Industry-aligned innovation: We tailor solutions to your domain - finance, healthcare, retail, or manufacturing - so your AI Agents solve real-world problems with sector-specific intelligence and resilience.
How Cazton Can Help You With AI Agents
Your organization has the opportunity to gain significant competitive advantage through strategic AI Agent implementation, but success requires more than technology deployment. It demands deep expertise in integration, customization, and business process optimization that generic solutions cannot provide.
For over a decade, we’ve been at the forefront of AI revolution, leading the way in developing AI-powered autonomous agents. We were the first company in the world to implement evals on GPT‑4 even before OpenAI. Our unwavering commitment to innovation has positioned us as thought leaders who set industry standards rather than follow trends. Since 2020, we have been at the helm of generative AI development, crafting agents that profoundly enhance and augment human capabilities across multiple sectors.
Our proven track record: We have successfully delivered AI solutions for Fortune 500 companies, large enterprises, mid-size organizations, and innovative startups. Our clients include Microsoft, Google, Broadcom, McKesson, First American Title, Fandango, Charles Schwab, AT&T, Thomson Reuters, Bank of America, Macquarie, Dell, and more - organizations that demand excellence and measurable results.
Collaborative excellence: Our team is composed of PhD and Master's-level experts in data science and machine learning, award-winning Microsoft AI MVPs, open-source contributors, and seasoned industry professionals with years of hands-on experience. We work closely with your teams to understand your specific requirements and craft solutions that integrate seamlessly with your existing workflows while delivering transformational capabilities.
Strategic value delivery: We understand that successful AI Agent implementation requires balancing cutting-edge technology with practical business value. Our approach ensures that your investment positions you for both immediate operational improvements and long-term competitive advantage.
Calling a language model API is easy. Building a robust, enterprise-grade Agentic AI system is not. At Cazton, we specialize in designing and deploying production-ready solutions that go far beyond simple API integrations.
Achieving success with AI requires more than just model access - it takes a sophisticated toolkit: advanced prompting strategies for high-precision outputs, agentic frameworks to orchestrate complex tasks, evals to monitor and benchmark performance, guardrails to ensure safety and compliance, and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) architectures that root responses in trusted, verifiable data.
We bring deep experience across modalities and systems - implementing full voice technology stacks, building asynchronous pipelines, handling data extraction and embeddings, and integrating with vector databases. Our team has worked with GraphDBs in tandem with LLMs, developed intelligent browser- and OS-level agents, leveraged the model-context protocol (MCP), and engineered reasoning models for intricate decision logic.
Here are our offerings:
- End-to-end AI Agent enablement: From strategy to architecture, agent design, deployment, and enterprise scaling - we support the full lifecycle of AI Agent adoption.
- Multi-agent systems at scale: We deploy collaborative agent ecosystems that work together across domains - unlocking intelligent automation for complex business processes.
- Human-in-the-loop design: We balance autonomy with oversight - building agents that support human teams and escalate critical decisions appropriately.
- Custom AI Agents for real-world use cases: We design intelligent agents for specific workflows - customer service, operations, compliance, and analytics - tailored to your business needs.
- Experience human-like interactions: Our AI Agents process text, voice, images, and video - enabling human-like interaction and perception across platforms and channels.
- Enterprise-grade agent orchestration: We implement agent planning, memory systems, tool use, and coordination logic to ensure autonomy, adaptability, and alignment with your goals.
- Secure, compliant agent deployment: Our frameworks integrate audit trails, access control, and encrypted memory - ensuring privacy, compliance, and enterprise trust.
- Platform-agnostic integration: AI Agents connect with your existing stack - whether you're on Azure, AWS, GCP, Snowflake, hybrid, or on-prem - with minimal friction and full extensibility.
- Rapid prototyping and validation: We build proof-of-concepts that demonstrate business value quickly - helping you test ideas and accelerate internal buy-in.
- Performance tuning and observability: We optimize agent response times, reliability, and behavior monitoring - enabling fast, consistent results at scale.
- Agent analytics and business insights: Our dashboards and reporting tools translate agent actions into measurable impact - giving leaders real-time visibility and control.
- Team training and AI agent readiness: We equip your teams with the skills, playbooks, and best practices to manage, extend, and evolve AI Agents confidently over time.
Partnering with us means working with a team that’s focused on delivering meaningful business outcomes through AI. The question is not whether AI Agents will transform your industry - it is whether your organization will lead that transformation or follow it. Contact us today to discuss how intelligent automation can revolutionize your business operations while positioning you for continued success in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
Cazton is composed of technical professionals with expertise gained all over the world and in all fields of the tech industry and we put this expertise to work for you. We serve all industries, including banking, finance, legal services, life sciences & healthcare, technology, media, and the public sector. Check out some of our services:
- Artificial Intelligence
- Big Data
- Web Development
- Mobile Development
- Desktop Development
- API Development
- Database Development
- Cloud
- DevOps
- Enterprise Search
- Blockchain
- Enterprise Architecture
Cazton has expanded into a global company, servicing clients not only across the United States, but in Oslo, Norway; Stockholm, Sweden; London, England; Berlin, Germany; Frankfurt, Germany; Paris, France; Amsterdam, Netherlands; Brussels, Belgium; Rome, Italy; Sydney, Melbourne, Australia; Quebec City, Toronto Vancouver, Montreal, Ottawa, Calgary, Edmonton, Victoria, and Winnipeg as well. In the United States, we provide our consulting and training services across various cities like Austin, Dallas, Houston, New York, New Jersey, Irvine, Los Angeles, Denver, Boulder, Charlotte, Atlanta, Orlando, Miami, San Antonio, San Diego, San Francisco, San Jose, Stamford and others. Contact us today to learn more about what our experts can do for you.